Building a website may feel overwhelming and confusing. Where do you even start? Of course, you want a site that is pleasing to the eye, but you also want it to have full functionality and be user-friendly – that’s where the WordPress content management system (CMS) comes into play. With its intuitive interface and extensive features, WordPress stands out as a widely acclaimed platform.
One of the easiest ways to dive into WordPress is by utilizing the WordPress.com platform.
This article will explore the main features of WordPress.com, look into its free and paid plans, and provide valuable insights to help you determine if it’s the right fit for your specific needs.
Table of Contents
- Relationship Between WordPress.com and WordPress.org
- WordPress.com Features
- How to Start Using WordPress.com
- WordPress.com Plans
- Pros and Cons of WordPress.com
- How to Migrate from WordPress.com to WordPress.org
- FAQ
- Conclusion
Relationship Between WordPress.com and WordPress.org
WordPress.org and WordPress.com both utilize the same underlying WordPress software but provide distinct services to users. Despite their close relationship, they are run by different entities and serve different purposes.
WordPress.org is the official website for a community-driven platform allowing users to download and use WordPress software freely. The WordPress software itself was initially created by Matt Mullenweg and Mike Little in 2003 as a fork of an earlier blogging platform called b2/cafelog. WordPress.org relies on a community of contributors who collaborate to improve the software, develop themes and plugins, and provide support.
In contrast, WordPress.com was also founded by Matt Mullenweg as a commercial venture. It allows users to create and manage websites without requiring technical setup. WordPress.com provides convenience and ease of use for beginners and non-technical users by handling hosting, security, updates, and backups. However, this convenience comes with some limitations on customization and plugin options compared to WordPress.org.
WordPress.com Features
WordPress.com offers many features available in self-hosted WordPress, but their number is limited to provide a simplified and manageable user experience. Additionally, the extent of available features depends on whether users are assigned to free or paid plans.
Let’s first look at what wp.com offers to free users, and we’ll get to the advanced features later in the article.
Content creation and management. WordPress.com offers an easy-to-use block editor with an intuitive drag-and-drop interface, allowing users to create and customize their websites without any coding knowledge. Various content blocks simplify adding and modifying text, images, videos, galleries, and visually appealing layouts.
Hosting and storage. Websites created on WordPress.com are automatically hosted on one of its servers. The platform ensures the websites are reliable and optimized for performance with regular updates and backups. Each free user gets up to 1GB of storage space.
Security. Each website on WordPress.com has integrated brute-force and spam protection, DDOS mitigation, and other safety tools to fight online security threats.
Subdomain. Users receive a free subdomain (e.g., yourwebsite.wordpress.com), allowing them to have a web presence without purchasing a custom domain.
Pre-designed themes. WordPress.com offers over 140 free professionally designed themes with diverse layouts and styles for various website types. Users can modify color schemes, fonts, and layouts to match their brand and personal preferences. Most themes are specifically made for blogs, businesses, and portfolio websites.
Mobile-friendly. The pre-designed themes are responsive, and all websites created on WordPress.com are automatically optimized for different screen sizes, ensuring a seamless experience for visitors on smartphones and tablets.
SEO tools. Every WordPress.com site includes basic SEO tools that help optimize websites for search engines, such as customizable meta tags, auto-generation of XML sitemap, and clean URLs.
Basic stats. Users can monitor website traffic and engagement, including the number of visitors and page views, helping them to understand their website’s success.
How to Start Using WordPress.com
Thanks to its simplified and intuitive approach, starting to use WordPress.com is a seamless and hassle-free process. No matter what type of website you want to create, these are the basic steps you will have to go through.
Signing up
To start building a website with WordPress.com, you must first sign up and create an account. Visit the official website and click the “Get Started” button. You’ll be guided through a simple signup process and asked to confirm your email address.
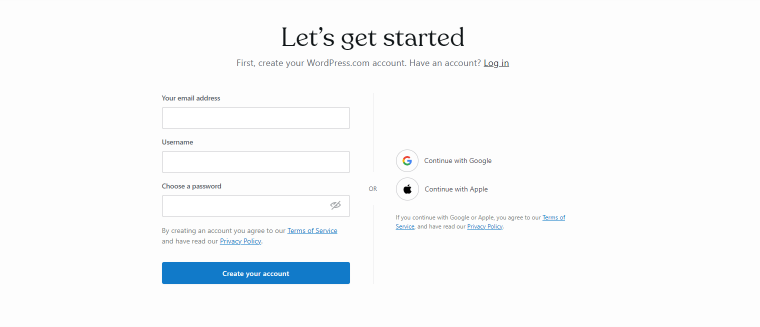
After the confirmation, you’ll see a WordPress dashboard area, and from there, you can get into your newly created site by clicking the “My Site” button in the top left corner of the page.
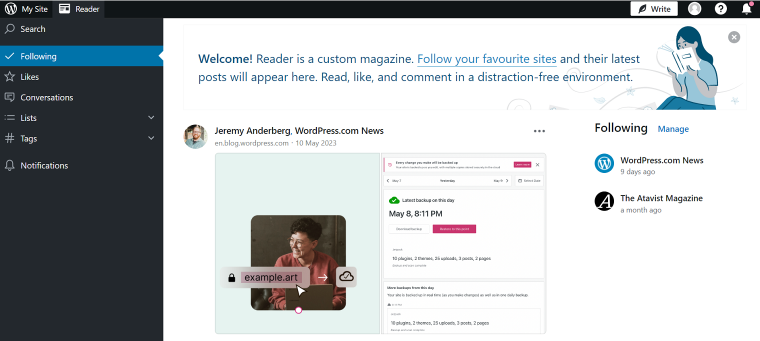
Your website is now visible to the public, and the site domain will look like mysite.wordpress.com, where the “my site” part of the domain will, by default, be the same as the username you chose during the registration process unless you opted for one of the paid plans.
Adding and editing content
Now you can access the website admin dashboard to add and modify the content.
The typical way to add content is by creating posts and pages. To create them, go to Pages > Add New and Posts > Add New. Most of the time, you’ll find Home, Contacts, and About pages on the websites. They are static, and you don’t need to create them often. On the contrary, use posts to add more timely content to a website and update them regularly.
Once you’ve created a post or a page, you can use blocks to edit its content. Blocks editor has a user-friendly interface that allows inserting new content by dragging and dropping various icons onto the working area. These blocks are designed to add different types of data: headlines, paragraph text, images, galleries, buttons, etc. After placing the block in the designated area, you can add the content by typing the text, uploading media files, and so on.
Each block has individual settings allowing you to control the appearance of the inserted content, and different types of blocks have different settings. For example, you can change font size, colors, and styles for text-related posts and add filters for image blocks.
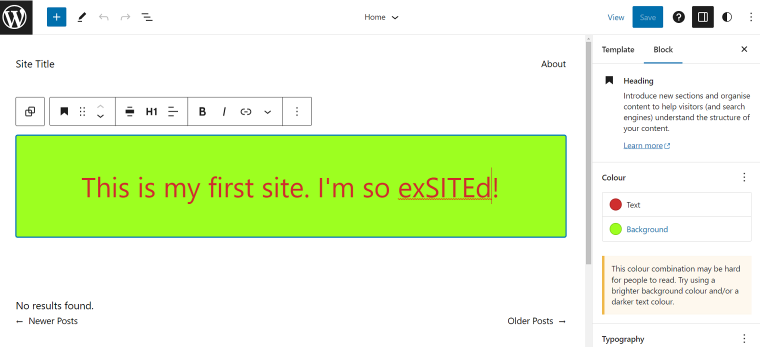
Creating a navigation menu
Finally, you must create a navigation menu for visitors to browse your website. Just insert a Navigation block where you want the menu to appear, and add and stylize links to created web pages. When you create a menu, all available page links will appear automatically. But, you must manually add a newly created page to an existing menu. Remember to create a menu with all the desired destinations and add it to every page to ensure easy navigation across your website regardless of the page you’re on.
NOTE
To check the visibility settings of your site, go to Settings > General > Privacy. If the Coming Soon option is selected, your site is hidden from viewers behind the “Coming Soon” notice, and if it’s in Private mode, only you and logged-in users will have access to the site.
WordPress.com Plans
WordPress.com offers free and paid plans, offering users options to suit their specific needs.
WordPress.com Free provides all the essential features for building a website. With this plan, users receive a WordPress.com subdomain (e.g., yoursite.wordpress.com) and basic hosting. Its biggest drawbacks are heavy WordPress.com advertising on your site, limited storage space, inability to use plugins to extend functionalities, and a limited number of available themes.
The Personal, Premium, Business, and Commerce paid plans provide varying levels of increased functionality and customization options.
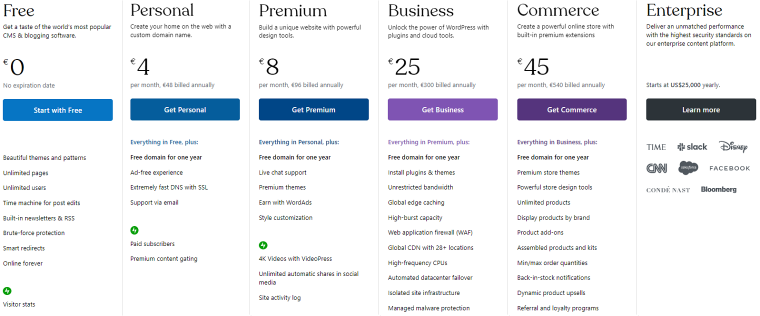
The first two plans are ideal for individuals who want to have simple but professionally-looking websites. They allow custom domain names, an ad-free experience, slightly increased storage space (6 & 13 GB), and access to WordPress premium themes. The Premium plan also lets you monetize your site with WordAds, the official WordPress.com advertising program.
The biggest upgrade the Business and Commerce plans offer is access to plugins and all of the WordPress.org themes, integration with advanced SEO tools, 200 GB storage space, and unrestricted bandwidth. Additionally, the Commerce plan includes essential features for building e-stores, such as integration with popular payment gateways and store customization tools.
NOTE
Even the most expensive WordPress.com plans don’t offer compatibility with all plugins. Some incompatibility issues are explained by the plugins’ redundancy or the possibility of them messing with WordPress.com SQL data, while I found no explanations for many other cases. You can read a partial list of incompatible plugins on WordPress.com’s official website.
WordPress.com offers monthly and annual prices. It’s cheaper if you have annual plans, starting from $48 per year for the Personal plan to $540 for the Commerce plan.
Pros and Cons of WordPress.com
So far, we’ve covered WordPress.com’s main features, dashboard characteristics, signup process, and paid plans. Now we are safe to summarize its advantages and limitations and compare WordPress.com with self-hosted WordPress to help you evaluate which option is the best fit for you.
Advantages of WordPress.com
WordPress.com offers several advantages when creating and managing simple or hobby websites.
- Ease of use: WordPress.com provides a user-friendly interface that simplifies website creation and content management. Its intuitive dashboard and native block editor enable users to create posts and pages without requiring coding knowledge.
- Convenience: WordPress.com takes care of hosting, security, and software updates, allowing users to focus on their content without the hassle of managing technical aspects. The platform provides free storage space and domain, handles server maintenance, and optimizes website performance, providing peace of mind to site owners.
WordPress.com limitations
Users should consider certain WordPress.com limitations, especially if they plan to build websites for business.
- Customization restrictions: users are restricted to the plugins available on the platform and cannot upload custom themes or use custom code.
- Monetization limitations: the ability to monetize your website is limited unless you buy the most expensive Commerce plan. Moreover, users on the Free plan have WordPress.com ads displayed on their site.
- Limited database access: WordPress.com doesn’t allow you to directly access your website’s database limiting your ability to perform advanced backend operations.
- Ownership and dependency on WordPress.com: With WordPress.com, you have neither full ownership nor control of the website, making you dependable on their infrastructure and service availability.
Comparing WordPress.com with WordPress.org
In short, the choice between WordPress.com and self-hosted WordPress boils down to convenience and control. On one side, you have a user-friendly platform ideal for beginners and those who prioritize ease of use. However, while handling hosting, updates, and security, wp.com limits customization, scalability, and monetization options.
On the other side, self-hosted WordPress offers users complete ownership and control over their sites, which requires more technical knowledge and responsibility.
If you want to know more about the difference between WordPress.com and WordPress.com, it’s best to read a detailed head-to-head comparison.
How to Migrate from WordPress.com to WordPress.org
Many beginners will start using WordPress.com but, after realizing its limitations, will look for a way to move to the self-hosted WordPress.org. Here are the key steps in the migration process.
- Get a WordPress hosting account and a domain name. In our blog, you can find articles about reliable domain registration providers and hosting providers specifically catered to WordPress sites.
- Export content from WordPress.com by navigating to Tools > Export > Export All. This allows you to export the whole site and download an export file to your computer.
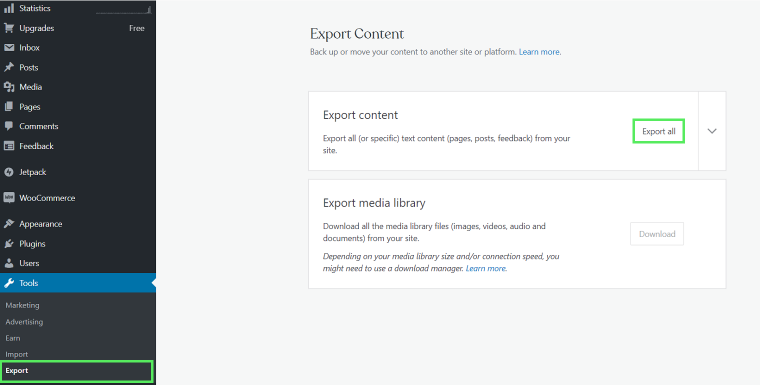
- On your newly created self-hosted WordPress site, go to Tools > Import > WordPress Install Now and click Run Importer. Then, you’ll be asked to upload the WordPress.com XML file created during Step 2.
- Now you should either set your WordPress.com site to private by going to Settings > General > Private, or, if you want to redirect your old visitors to a new site, go to Settings > General > Redirect and enter the site domain. However, WordPress.com will charge you $13 per year for the redirection service.
FAQ
Yes, WordPress.com offers a free plan allowing creating and hosting basic websites. There are also paid plans available that provide additional features.
Yes, with the paid plans on WordPress.com, you can use a custom domain name for your website.
You can monetize your WordPress.com website through the WordAds advertising program available on some paid plans, which allows you to display ads and earn revenue. However, the ability to use third-party ad networks is limited, and it’s only available on the most expensive Commerce plan.
The ability to install plugins is available only on the Business and Commerce plans of WordPress.com. Not all the plugins available on WordPress.org can be installed on WordPress.com.
Conclusion
In conclusion, WordPress.com is a great platform for building simple websites with its user-friendly interface and free plan option. The highest-tier plans on WordPress.com provide functionality that comes close to self-hosted WordPress, offering more control and flexibility. However, it’s essential to consider the cost and convenience factors as for users seeking complete ownership, unlimited optimization options, and scalability, opting for WordPress.org might be a better choice.

